Sex Hormones - Pregnancy
Sex hormones are responsible for some of the most dramatic changes that occur in the body. They control puberty, egg and sperm production, pregnancy, birth and lactation (breastfeeding).
Pregnancy

If a fertilised egg starts to grow in the uterus, that is, the woman is pregnant, her periods stop.
This happens because, during pregnancy, progesterone continues to be produced. This maintains the thicker lining of the uterus and stops the development of any more eggs in the ovaries.
Birth and Breastfeeding
When the baby has been growing for about 9 months, the pituitary gland produces a hormone called oxytocin which starts contractions of the uterus.
At birth the level of progesterone falls and the pituitary produces another hormone, prolactin which causes the production of milk. Oxytocin and prolactin are involved in the ejection of milk from the breasts and the continued production of milk throughout breastfeeding.
In-Vitro Fertilisation (IVF)
Sometimes a woman is unable to become pregnant. If this is due to eggs not maturing in the ovaries each month, it can be treated with FSH. As the name suggests, this hormone stimulates the follicles in the ovaries to produce mature eggs.
It might be necessary to remove the mature eggs from the woman´s body and mix them with sperm in a laboratory. This is known as In-Vitro Fertilisation (IVF). Some of the fertilised eggs that result from IVF are then placed in the woman´s uterus where they can develop as normal.
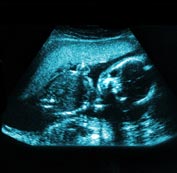
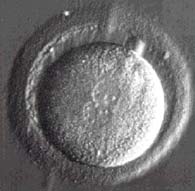

Images courtesy of Newcastle Fertility Centre at LIFE
Contraception
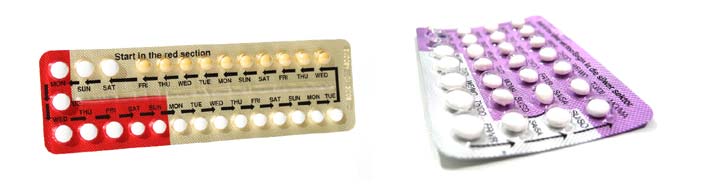
To stop pregnancy from happening, the contraceptive pill can be taken. This contains female sex hormones, often a combination of oestrogen and progesterone, which prevent ovulation by mimicking pregnancy.
The Menopause and HRT
When the ovaries stop producing eggs (usually in a woman´s 50s) there is a drop in the production of the female sex hormones. This causes changes in a woman's body (known as the Menopause), some of which, such as hot flushes, night sweats and mood swings, may be uncomfortable. HRT, Hormone Replacement Therapy, is prescribed to relieve these symptoms.
Usually HRT is a mixture of oestrogen and progesterone, the oestrogen to relieve the symptoms and the progesterone to protect against cancer of the uterus. If the woman has had her uterus removed, then an oestrogen only pill can be used. Previously equine oestrogen and a synthetic progesterone were used. Now, because we have the advantage of genetic engineering, the use of human sex hormones is possible.
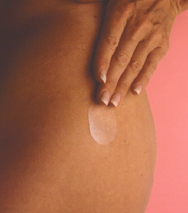
Recent research has shown that there are increased risks of developing bloods clots and cardiovascular problems associated with certain types of HRT. It is thought that some of the potential problems could be minimised by applying HRT to the skin rather than being taken as tablets. Also alternative therapies are being considered, for example:
- The use of human oestrogen and progesterone
- Life-style changes
- Non-hormone drug therapies
- Dietary changes
- Increased amounts of exercise