Sex Hormones - The Menstrual Cycle
Sex hormones are responsible for some of the most dramatic changes that occur in the body. They control puberty, egg and sperm production, pregnancy, birth and lactation (breastfeeding).
The Menstrual Cycle
Approximately once a month girls experience menstruation which is bleeding through the vagina. This is caused by the breakdown of the lining of the uterus (womb) and is part of the cycle of events called the menstrual cycle.
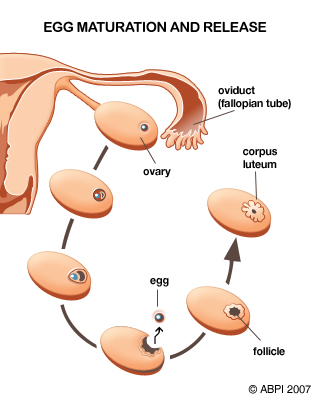
The cycle starts with menstruation and then gradually a new egg develops in one of the ovaries. About 14 days after menstruation started the new egg is mature and leaves the ovary (a process known as ovulation). The egg travels down an oviduct (fallopian tube) where, if it meets a sperm, it may be fertilised.
By this time in the cycle the wall of the uterus has repaired itself and thickened up again ready to receive the fertilised egg. The fertilised egg enters the uterus and continues to grow into a baby. If the egg is not fertilised it disintegrates and leaves the body with blood and uterus lining during the next period.
Hormones Control the Menstrual Cycle
Hormones are involved at every stage of the menstrual cycle.
- The pituitary gland produces FSH which starts the development of one egg in a follicle in one of the ovaries.
- The ovary produces oestrogen which causes the repair of the lining of the uterus after the last menstruation.
- The pituitary now produces LH which causes ovulation and stimulates the empty follicle to produce progesterone.
- Progesterone causes the lining of the uterus to get thicker ready for the fertilised egg.
- If the egg is not fertilised, production of oestrogen and progesterone stops, the lining of the uterus breaks down and menstruation occurs.
Question 3


To reorder an item; select it, then use the up or down arrow to the right of the list to move it.
The first answer is already set for you at the top of the list.